Understanding Foundation Design Codes and Standards for Slab Foundations
Foundation design is a critical aspect of any construction project, and adhering to the right codes and standards is essential for safety and durability. This article explores the key foundation design codes and standards, with a focus on slab foundations, and provides practical insights for ensuring compliance.
Foundation design codes and standards are a set of regulations and guidelines that dictate how foundations should be designed and constructed. These codes are developed by organizations like the International Code Council (ICC) and the American Concrete Institute (ACI) to ensure that foundations are safe, stable, and able to support the structures built on them. For slab foundations, which are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings, these codes specify everything from the thickness of the slab to the type of reinforcement required.
Adhering to foundation design codes and standards is crucial for several reasons. First, they ensure the safety of the building and its occupants by preventing structural failures. Second, they help maintain the integrity of the structure over time, reducing the risk of costly repairs. Finally, compliance with these codes is often required by law, and failing to meet them can result in legal and financial consequences.
Several key codes and standards apply to slab foundations. The International Building Code (IBC), published by the ICC, is one of the most widely adopted codes in the United States. It provides comprehensive guidelines for foundation design, including requirements for slab thickness, reinforcement, and load-bearing capacity. The ACI 318 standard, developed by the American Concrete Institute, is another critical resource, offering detailed specifications for concrete slab foundations. Additionally, local building codes may have specific requirements based on regional conditions, such as soil type or seismic activity.
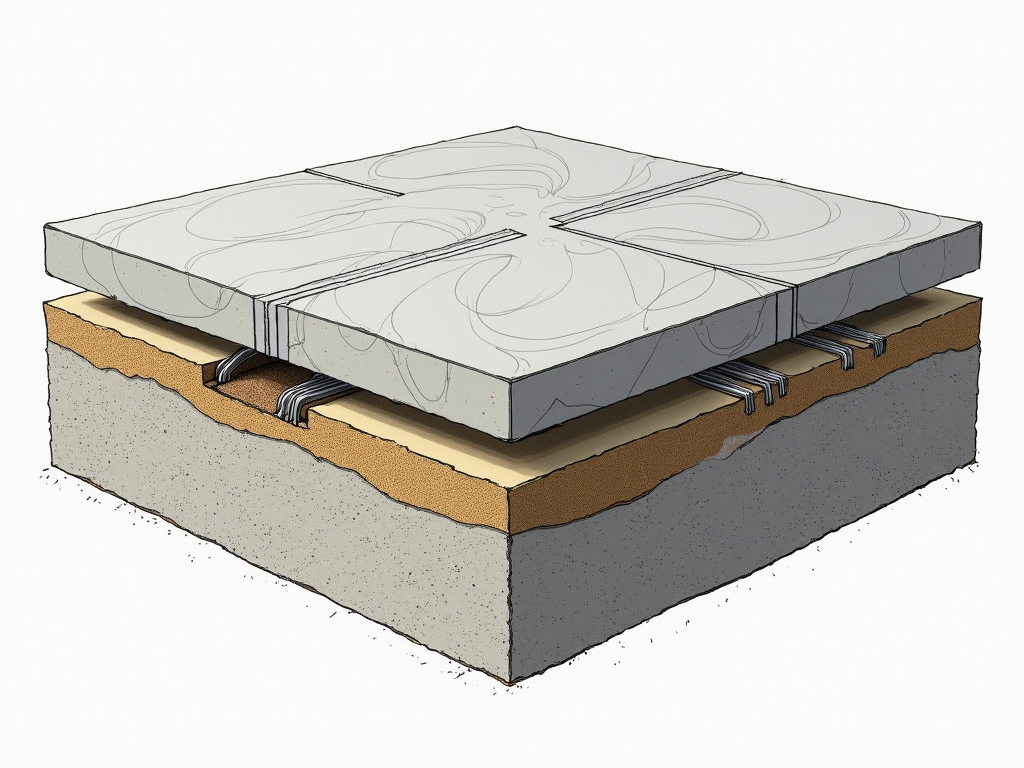
Applying foundation design codes and standards involves several steps. First, you need to determine the specific codes that apply to your project based on its location and type. Next, you should consult the relevant code documents to understand the requirements for slab foundations. This may include calculating the required slab thickness, determining the type and amount of reinforcement needed, and ensuring proper soil preparation. It's also important to work with a qualified engineer or designer who is familiar with these codes to ensure compliance.
One common mistake in foundation design is underestimating the importance of soil testing. The type of soil beneath a foundation can significantly impact its performance, and failing to account for this can lead to issues like settling or cracking. Another mistake is not providing adequate reinforcement, which can result in a weak foundation that can't support the structure's weight. To avoid these mistakes, always conduct thorough soil tests and follow the reinforcement guidelines specified in the relevant codes.
In my experience, one of the most challenging aspects of foundation design is balancing cost with compliance. For example, in a recent project, we had to decide between using a standard slab thickness and increasing it to meet local code requirements for seismic activity. While the thicker slab was more expensive, it provided added safety and peace of mind. This experience taught me the importance of understanding the rationale behind code requirements and not just following them blindly.
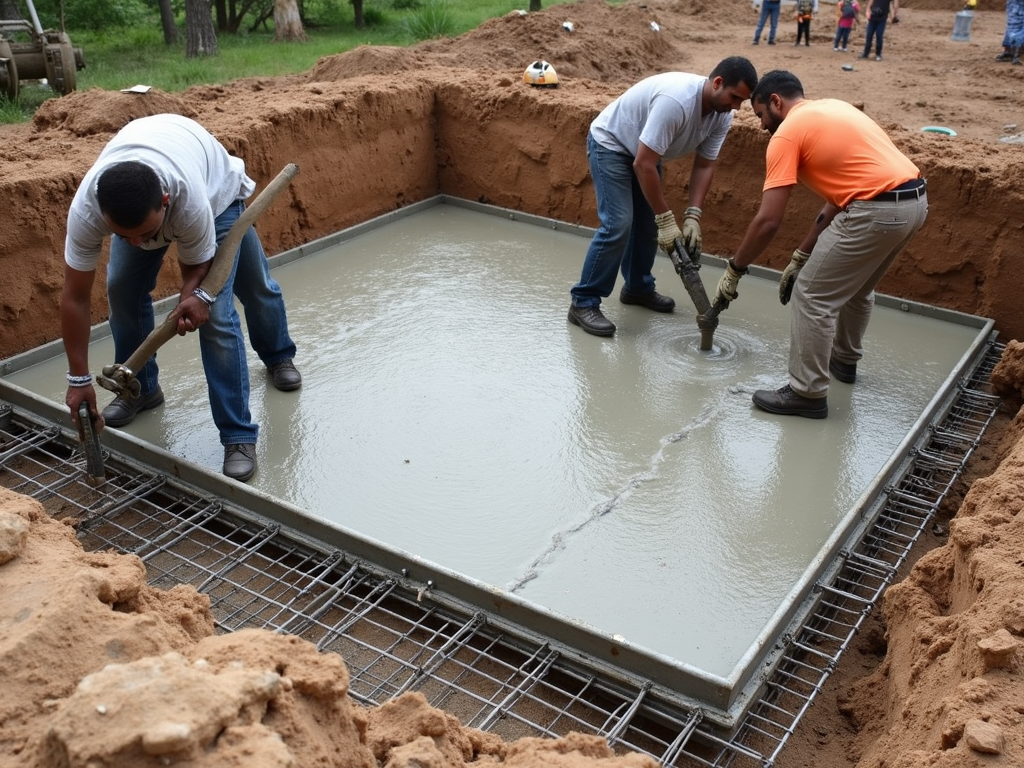

Foundation design codes and standards are essential for ensuring the safety, stability, and longevity of slab foundations. By understanding and applying these codes, you can avoid common mistakes and ensure your foundation meets industry standards. Remember to consult the relevant codes for your project, work with qualified professionals, and prioritize safety over cost.





