Mastering Structural Design Principles for Civil Engineers
TL;DR
Discover fundamental structural design principles for civil engineers, focusing on slab design and footing calculation, with practical insights and clear guidance.
Introduction to Structural Design Principles
Structural design in civil engineering forms the backbone of creating buildings and infrastructure that stand the test of time. For engineers, mastering design principles is crucial to ensure stability, efficiency, and safety in their projects. This article delves into core principles, with a firm focus on slab design and footing calculation, offering practical insights based on real-world experiences.

Understanding Load Path and Load Types
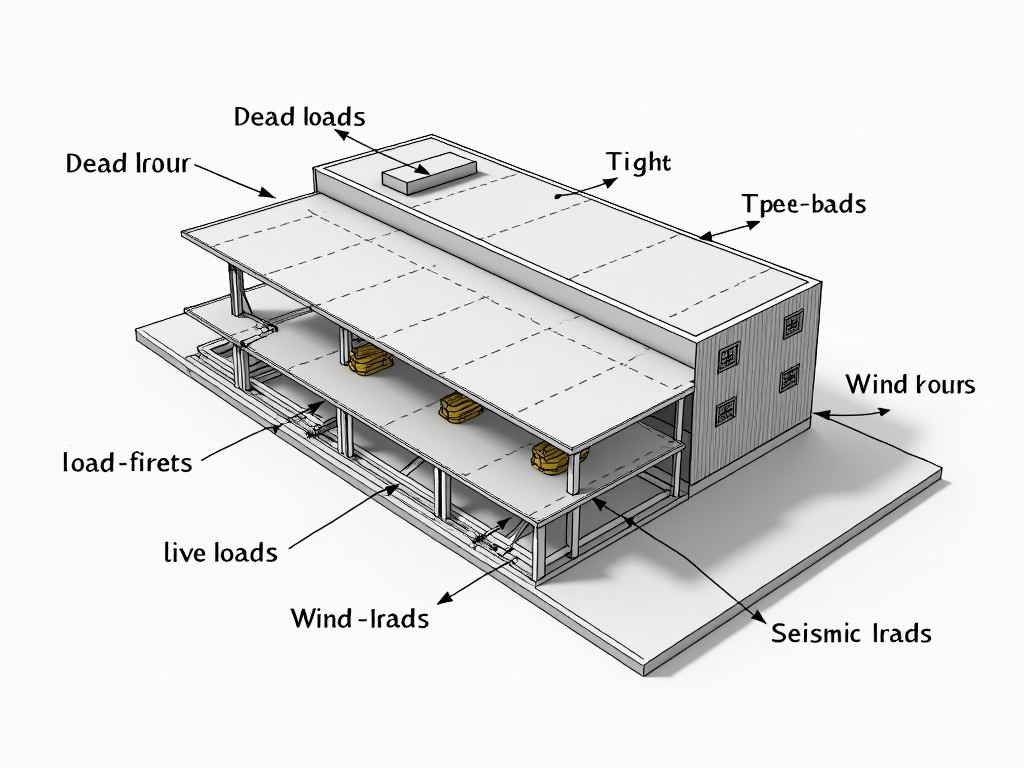
One of the fundamental concepts in structural design is understanding the load path, which refers to the path through which loads are transferred from floors and roofs down to the foundation. This knowledge ensures that every part of the structure supports what it needs to. Different types of loads need consideration, including:
- Dead Loads: Permanent static forces from the building structure itself.
- Live Loads: Variable forces from occupancy and usage.
- Environmental Loads: Impacts from wind, seismic activity, or snow.
Slab Design Considerations
Slabs are critical components affecting both functionality and aesthetics. They must withstand substantial forces without compromising stability. Here are some essential considerations:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material mix balances durability and cost efficiency.
- Thickness and Reinforcement: These determine the slab's ability to bear and distribute loads effectively.
- Support and Span: Understanding support placement minimizes deflection under weight.
Footing Calculations and Stability
Footing is the foundation that supports structures by transferring loads to the ground. Correct footing calculation is essential for avoiding settlement and ensuring long-term durability.
- Soil Analysis: Conducting thorough soil tests provides data on load-bearing capacity.
- Footing Size and Depth: Calculations are based on expected loads and soil conditions.
- Reinforcement: Ensures the stability of the footings, particularly in diverse soil conditions.

Practical Experience: Insights from the Field
Having worked on numerous projects, it becomes apparent that:
- Attention to Detail: Minor miscalculations can lead to significant challenges.
- Collaboration: Effective communication with geotechnical teams improves footing accuracy.
- Adapting to New Technologies: Leveraging advancements like computer-aided design (CAD) tools enhances precision and efficiency.
Summary
Structural design principles for civil engineers are both an art and a science. From understanding load paths to executing detailed slab designs and precise footing calculations, each step is vital to a project’s success. Always remember to integrate expert insights and adopt a proactive approach for adapting to new challenges.

Recommended Readings on Structural Design
For those looking to delve deeper, consider these thorough reads:





