Mastering Foundation Footing Calculations: Essential Methods and Tips
Understanding the Basics of Foundation Footing Calculation
Foundation footing calculation is crucial for ensuring the stability and durability of a building. This article explores various methods used in slab foundation and overall footing calculation, providing insights into ensuring structural safety and longevity.

When it comes to constructing a new building, understanding the underlying principles of foundation footing calculation is essential. A well-calculated footing ensures that the building's load is evenly distributed across the foundation, avoiding unnecessary stress that could lead to structural failure. But what exactly does this calculation entail? Let's delve deeper into the process.
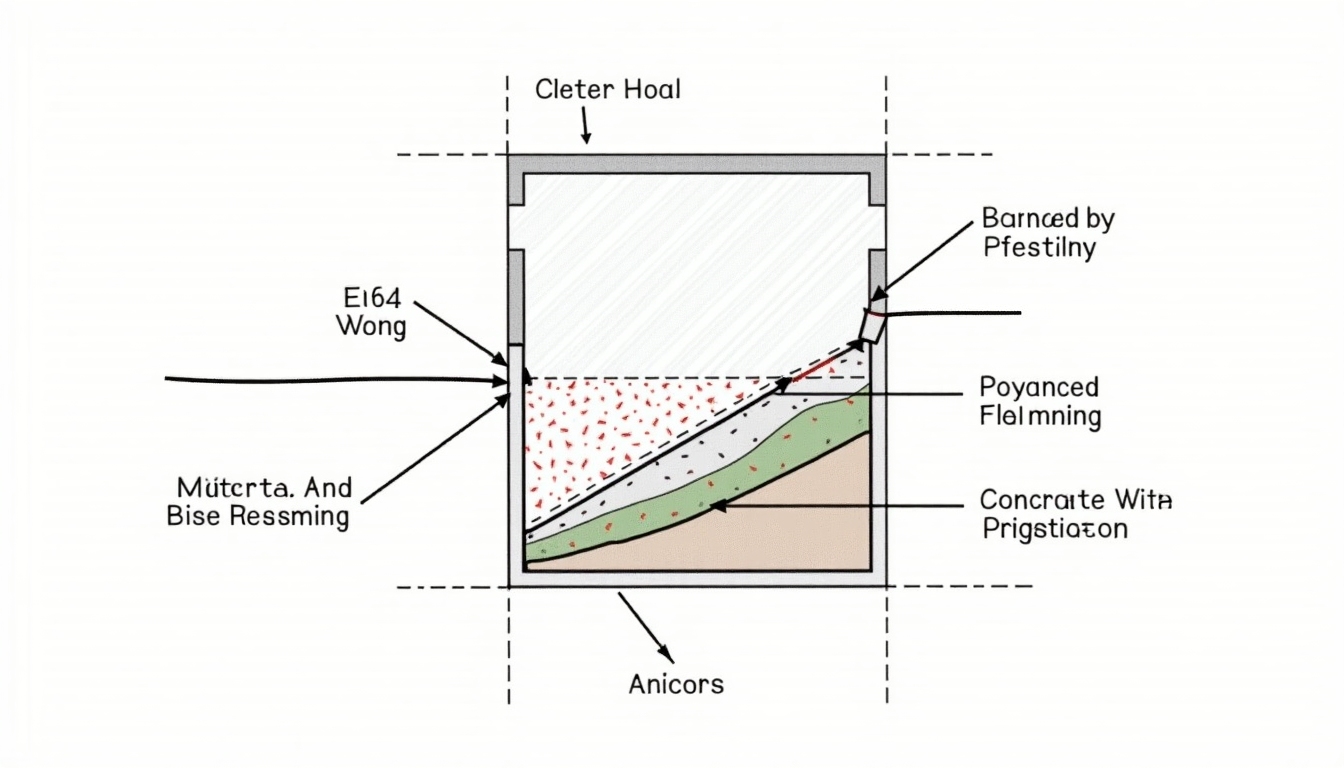
Key Components of Foundation Footing
Foundation footing is simply the base that supports the foundation of your home. There are several components and steps involved in calculating the right footing for your construction project, which are crucial to understanding:
- Load Bearing Capacity: This refers to the soil's ability to support the weight of the building. It is crucial to assess this as different soils have varying capacities.
- Slab Foundation: Involves a single, thick layer of concrete poured directly onto the ground. This method is popular in warmer climates.
- Footing Depth and Width: Calculating the correct depth and width is critical to distribute the load evenly.
Let’s explore these components in more detail to understand how they contribute to the entire process.

Methods of Foundation Footing Calculation
There are various methods used by professionals to ensure the footing is calculated accurately:
1. Empirical Methods
These are based on historical data and involve the use of established standards and guidelines. While simple, these methods provide a general guideline and are often used for smaller projects.
2. Analytical Methods
These methods involve mathematical equations and principles grounded in physics and engineering. They offer precise measurements and are used in larger or more complex structures.
- Rankine’s Formula: Often used for designing retaining walls and calculating bearing pressures.
- Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity Theory: Utilized for determining the load-bearing capacity of soil.
Let's take a closer look at each of these methods to understand their applications.

Hands-On Tips for Calculating Footing
Successfully calculating the footing requires more than just understanding the theory. Here are some actionable insights:
- Conduct Proper Soil Tests: Before any calculation, perform a thorough soil test to understand its load-bearing capacity.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Seasonal changes can affect soil properties, impacting footing stability.
- Use Appropriate Materials: The choice of materials such as concrete mix should suit the environmental conditions and load requirements.
These tips help enhance the accuracy of your calculations and lead to safer and more durable construction.

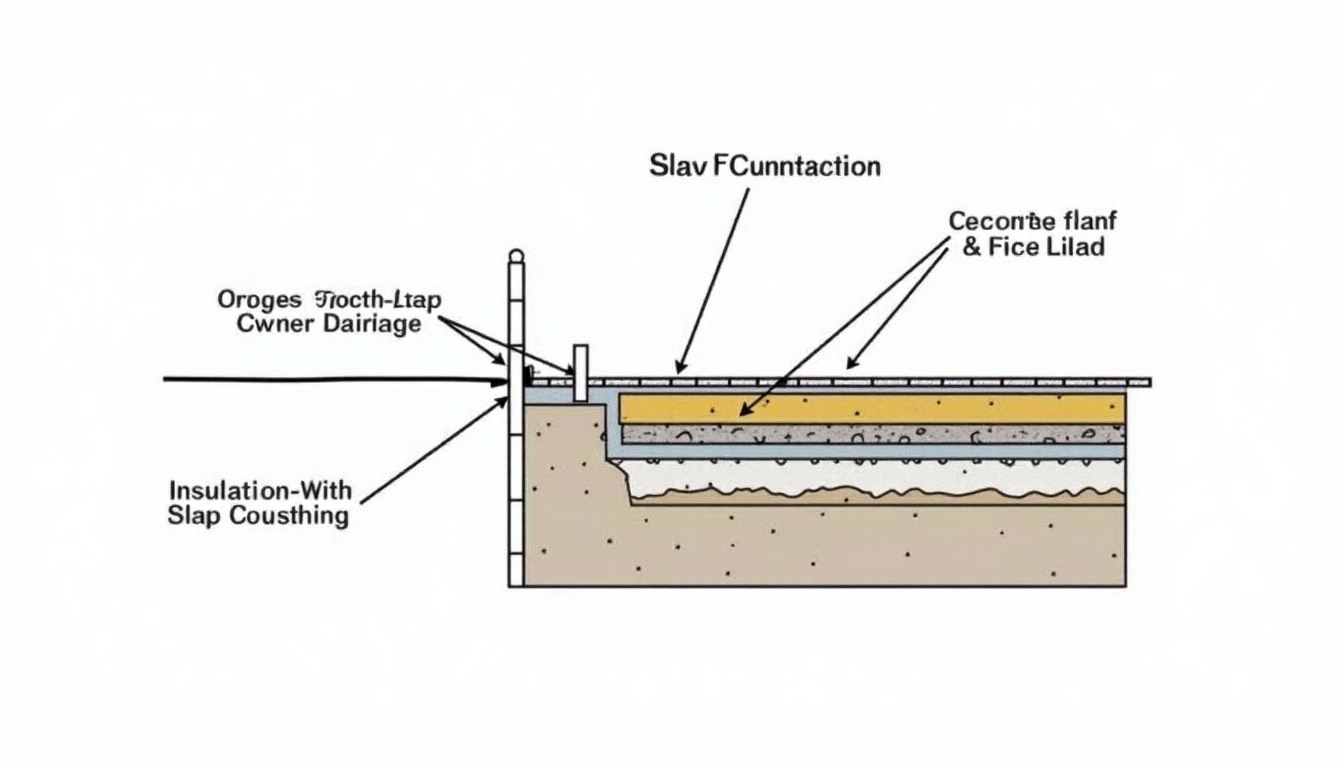
The Importance of Slab Foundation
A slab foundation is a monolithic pour of concrete, providing a solid base for most structures, particularly in areas with uniform ground levels and climates. Here’s why it’s favored:
- Reduced Cost: Slab foundations typically cost less than other types, such as raised or basement foundations.
- Time Efficiency: Requires less time to construct given the fewer steps involved.
- Pest Resistance: Lacks a sub-floor space, minimizing pest access.
Conclusion: Ensuring Structural Stability
Ensuring the accuracy of your foundation footing calculation not only safeguards the structural integrity of your building but also increases its lifespan and safety. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or a construction enthusiast, understanding these fundamentals equips you to oversee and implement more effective building strategies.





